The Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) and Sound Transmission Class are two values that are typically shown on items when you want to purchase acoustic or soundproofing materials (STC).
Have you ever considered what these two numbers signify in sound design and why they are labelled on every product?
Yes, or No.
If you’re reading this article, it suggests you’re interested in understanding both of these ideas and we call Impact insulation class (IIC), which will also address the same.
In conducting a soundproofing study, I went through many characteristics everywhere to measure the soundproofing quality of material, and the very best statistics that mattered a lot were NRC and STC.
Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) Vs Sound Transmission Class (STC):
Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC):

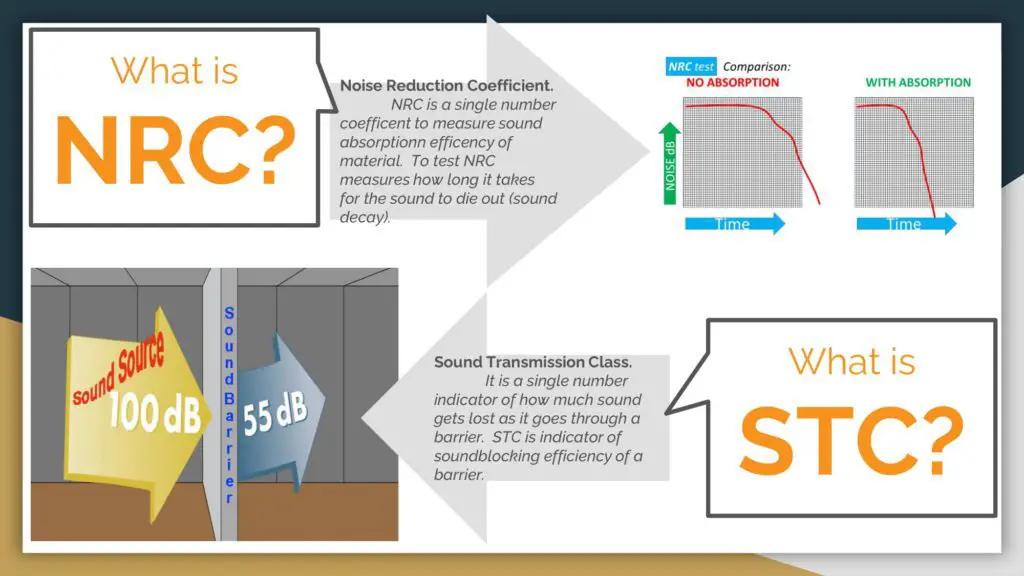
An NRC is a rating that indicates how much sound an acoustic product can absorb on average.
An acoustic product absorbs sound in the same way as a sponge absorbs water, and the NRC specifies how much sound certain goods can absorb.
The noise reduction coefficient (NRC) referred to as the noise reduction factor (NRF) is the ratio of the average logarithmic attenuation or decay rate (dB/s) of sound frequencies between 250, 500, 1000, and 2000 Hz caused by sound-absorbing objects in a region to the area without any such objects.
The NRC value essentially describes a material’s capacity to absorb sound waves with frequencies ranging from 100 Hz to 5000 Hz.
The NRC is assigned a value between 0 and 1. An NRC of 0 means that the product absorbs no sound.
An NRC of 1 indicates that the product completely absorbs all sound, the greater the NRC, the better the product absorbs sound.
It is not easy to calculate the NRC of an acoustic product.
There are several methods for determining NRCs; the following describes how our goods are evaluated for NRC utilizing the ASTM Standard Test Method for Sound Absorption.
- A sound test lab room particularly built for testing sound absorption is outfitted with a microphone and sophisticated sound frequency monitoring equipment.
- To begin the test, a noise signal is transmitted into the room and the device measures how much sound is absorbed.
- A second measurement of the product’s sound absorption at four different frequencies is taken after the original measurement at the same testing facility.
- The NRC is determined by averaging the numerous readings and rounding to the closest 0.05.
The following materials have NRC references:
If the NRC is 0.1, it signifies that the material can absorb 10% of the sound waves but will reflect 90% of the back.
- 0.00-0.05 NRC Brick.
- 0.05 NRC for glass.
- NRC 0.10-0.15 Plywood.
- 0.20-0.30 NRC for carpet over concrete.
- 0.30-0.50 NRC carpet with a foam pad.
Sound transmission class (STC):

STC (sound transmission class) is a measurement used to determine the efficacy of soundproofing materials in minimizing sound transmission between rooms.
STC is the amount of noise reduction (dB) that material or partition may give to establish the amount of sound.
For instance, a wall will be able to block it from reaching the other side.
The transmission loss data is obtained and tested at 18 of the most common frequencies (between 125 Hz and 4000 Hz) to build a curve, which is then compared to the corresponding STC curves of references.
Your specific fixture’s STC rating is calculated by the curve of reference that your curve most closely follows.
A wall is said to have an STC of 40, for instance, if one of its curves most closely resembles the standard STC 40 curve.
The higher the STC rating, the more effective the substance is in reducing sound transmission at the most common frequencies.
- Decibels (dB) – A decibel (dB) is a standard unit of measurement for loudness, frequency is described as the measurement of a sound’s time or musical note.
- Transmission Loss – The difference in loudness (dB) on each side of the wall is measured as transmission loss.
Here are a few illustrations that show how the transmission of sound may be affected by any material’s STC score.
- 25 – Audible normal speech.
- 30- Normal speech is difficult to understand, while loud speech is audible.
- 35 – Loud Speech, but not audible
- 60 – Loud Music is hardly audible.
- 70- Power tools may be heard faintly.
- 75+ The majority of noises are utterly inaudible.
These STC ratings above show that the higher the number, the better the ability to block sound waves.
Two basic methods are employed to raise the soundproofing STC score.
Isolation: Using a resilient channel to build a hollow wall with two layers of drywall.
Adding Mass: By adding more mass to an existing wall is accomplished using the Mass loaded vinyl (MLV).
What is the Difference between NRC and STC?
The noise reduction coefficient (NRC) is associated with the material’s capacity to absorb noise and is frequently rated on a scale of 1 to 10, whereas the sound transmission class (STC) is associated with the blocking capability of any substance, particularly isolating material used as a separation, and evaluated on a scale of 100.
If you’re having trouble with noise from your neighbour and want to overcome it, consider the STC score rather than the NRC when selecting a soundproof material.
But, if you want to increase the sound quality in your home or room, it is advisable to focus on eliminating echoes by absorbing sound waves rather than STC.
To absorb as much noise as possible, materials like carpet, mats, or acoustic foam are utilised in the gym’s ceiling, walls, and other areas, and NRC is mostly required for these materials.
The STC score will be important in areas where you wish to keep your conversation private from others on the opposite side of the private zone.
Examples include things like insulating materials, Drywall, or green glue used to build walls.
Also read: Difference between Pink Noise and White Noise
FAQ- Difference between NRC and STC:
Q1. What is a good NRC rating?
Best – 0.90, Better – 0.80, Good – 0.70, Avoid less than 0.70 NRC.
If there are a lot of people or equipment in the space and noise or reverberation might interfere, strong noise absorption is critical.
Use the 0.90 Best NRC category.
Q2. What is an effective noise reduction coefficient?
An effective noise reduction coefficient is normally more than 0.45, but it also depends on how much sound absorption is required in the space.
Q3. What is the highest STC rating available?
The STC rating ranges from 0 to 65.
Most devices do not guarantee anything over a grade of 55, and even a rating of 60 does not ensure complete soundproofing.
Also read: Difference between Resilient Channel and Hat Channel
Conclusion:
Sound absorbing is a component of soundproofing that implies completely soundproofing any place.
You must also consider sound-absorbing materials, it is preferable to understand both STC and NRC.
STC should be prioritized if you are seeking for solutions to avoid sound transmission to the opposite side of your region, while NRC will assist you to increase sound quality by absorbing noise.
Mostly every soundproof material will have these two characteristics, so evaluate their ratings and make sure to place a purchase order for the same depending on the necessity.
Please tell our readers about your experience with NRC ratings in your particular noisy environment so they may have faith in the NRC and STC ratings as being accurate and up to grade.
Section Under: Diff









